Analogue GPR study of the Permian fanglomerates from Zygmuntówka Quarry near Chęciny, Holy Cross Mountains, southern Poland, for construction of a training image for multiple point simulations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7306/gq.1438Keywords:
alluvial fans, ground penetrating radar, Permian conglomerates, sedimentary facies, multiple-point statistics, training imageAbstract
The distribution of Permian alluvial fan lithofacies in a quarry at Zygmuntówka near Chęciny, Holy Cross Mts., in southern Poland was investigated using ground penetrating radar (GPR) in order to create a training image for multiple point statistics (MPS) reconstructions of alluvial fan sedimentary facies. Five pseudo-3D GPR datasets were collected, processed and uploaded for interpretation into SKUA-GOCAD 3D geological modelling software. Three radar facies were distinguished based on the 3D geometrical pattern of radar reflections and linked to lithofacies described from the quarry by Zbroja et al. (1998). A statistical summary showed that ~50% of the lithofacies resulted from gravity flows (mostly non-cohesive), while the remaining proportion was deposited by unconfined and confined flash floods. Fluvial sedimentary facies left by waning of catastrophic floods or reworking during fair weather, although not prevalent, could not be distinguished from confined flood deposits based only on GPR data. The GPR datasets together with information from field observations were used to carry out MPS simulations and estimate the most probable 3D model of lithofacies at the quarry scale. This model will in turn serve as a training image for MPS reconstructions of alluvial-fan facies of Rotliegend conglomerates in the multi-scale geological model of the Gorzów Block (western Poland).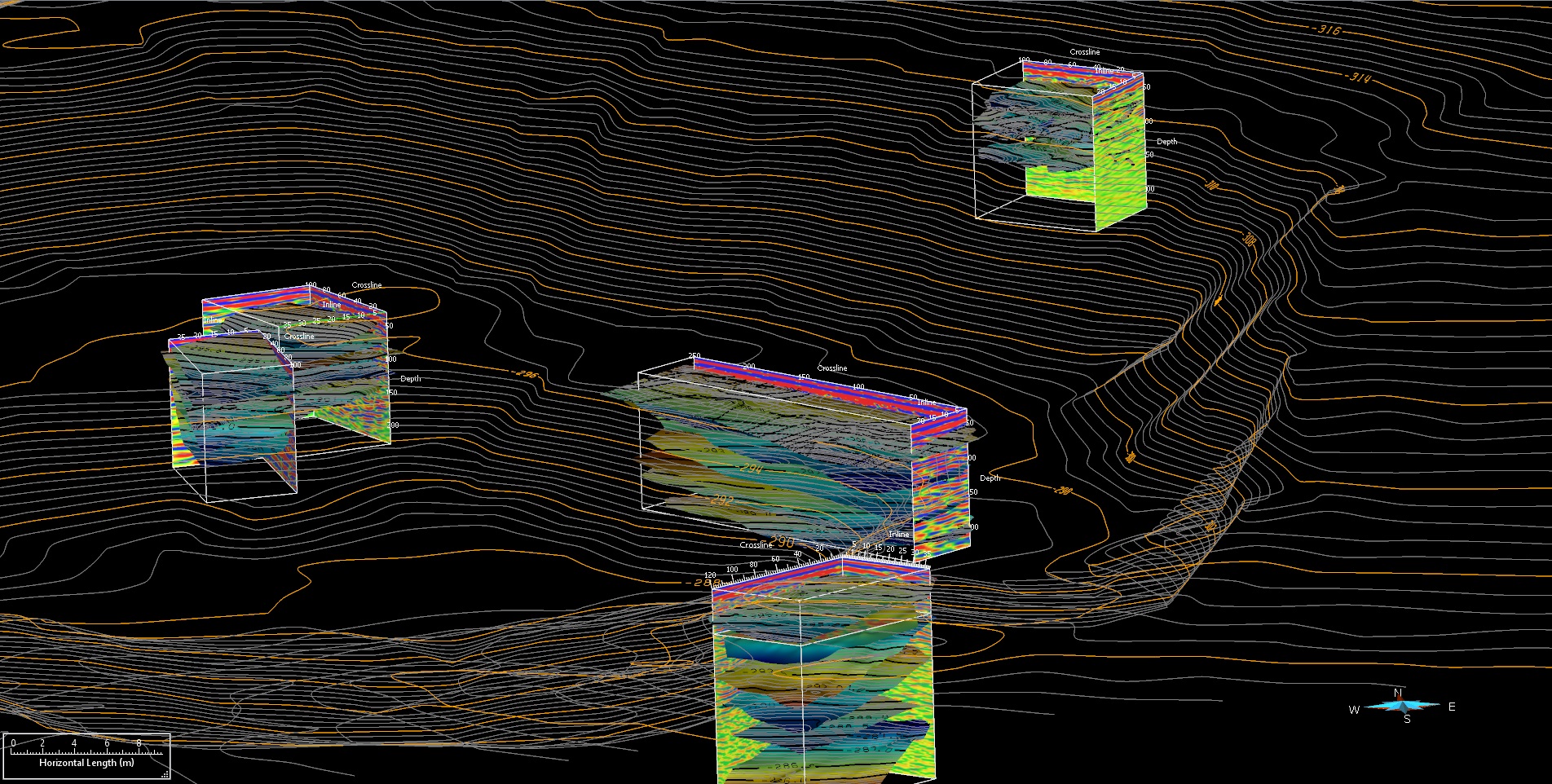
Downloads
Published
2018-11-30
Issue
Section
Articles
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as this can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and more frequent citation of the published work (See The Effect of Open Access).





